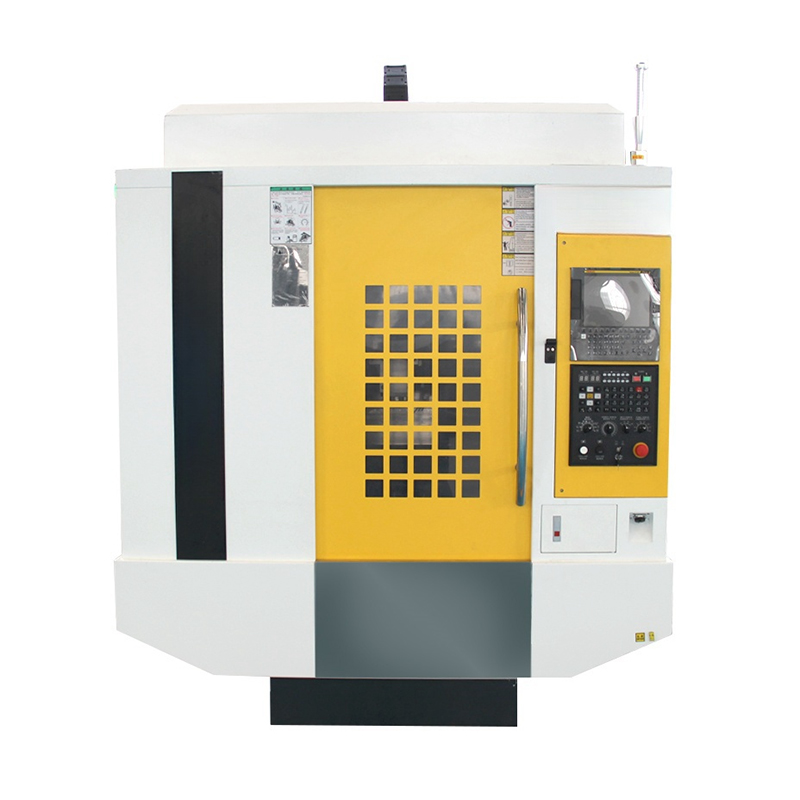
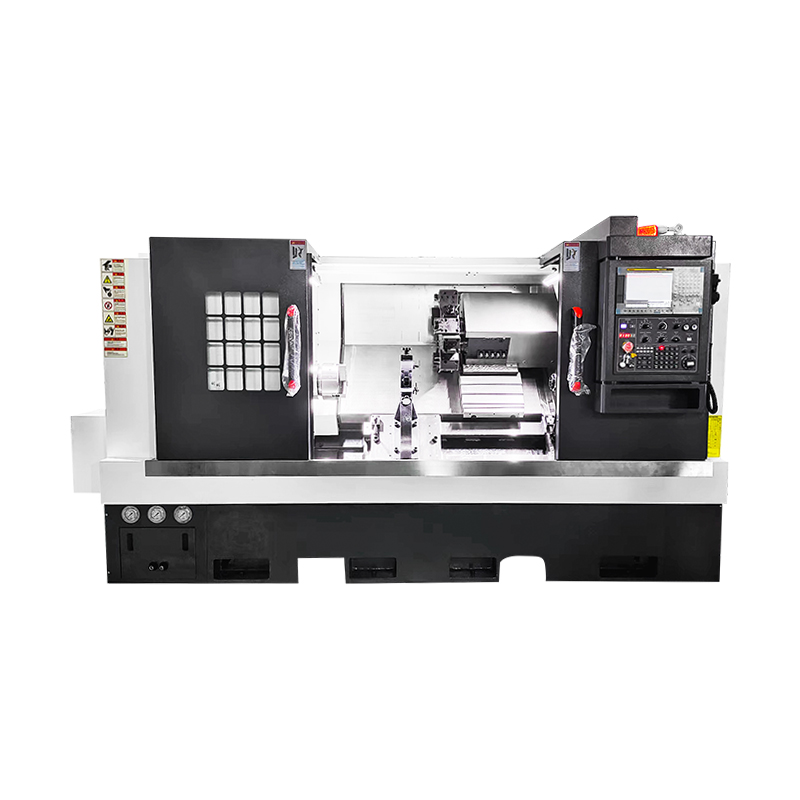
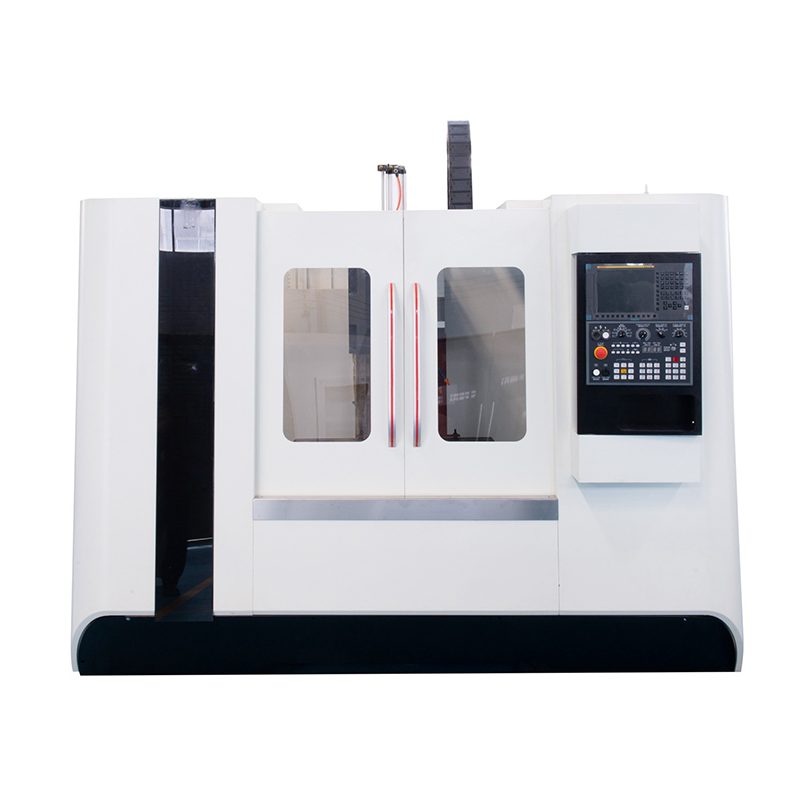
In today's highly automated industrial environment, CNC Machine has become an indispensable core equipment in the manufacturing industry. This technology, which perfectly combines computer control with traditional mechanical processing, has not only completely changed the way products are manufactured, but also brought a qualitative leap in industrial productivity. From aerospace to medical devices, from automotive parts to consumer electronics, the precision processing capabilities of CNC machine tools support all aspects of modern industry.
The core of CNC technology lies in converting digital instructions into mechanical movement. Unlike traditional machine tools that rely on manual operation, CNC systems control tool paths, speeds, feed rates and other parameters through pre-programmed codes to achieve highly automated precision processing. This technology originated in the late 1940s and was originally developed to meet the urgent needs of the aerospace industry for complex parts processing. With the advancement of computer technology, CNC systems have undergone an evolution from punched paper tapes to magnetic media to modern fully digital control systems.
Contemporary CNC systems usually consist of three main parts: control unit, drive system and feedback device. The control unit is responsible for interpreting the machining program and generating control signals; the drive system includes servo motors and transmission mechanisms, which convert electrical signals into mechanical motion; the feedback device monitors the machine tool status in real time through sensors such as encoders or grating rulers, forming a closed-loop control system to ensure machining accuracy. This precision control mechanism enables modern CNC machine tools to achieve micron-level or even nanometer-level machining accuracy.
According to the machining method and functional characteristics, CNC Machine can be divided into multiple categories, each with its own unique technical advantages and applicable fields. Milling center is one of the most common CNC equipment. It can complete the machining of complex three-dimensional contours by removing materials through rotating tools. Turning center is mainly used for the machining of rotationally symmetrical parts. The workpiece rotates while the tool moves. It is suitable for the precision manufacturing of shaft and disc parts. Multi-axis machining center represents the highest level of CNC technology. By increasing the number of rotating axes, multi-faceted machining can be completed in one clamping, which greatly improves the manufacturing efficiency and accuracy of complex parts.
The efficient operation of CNC Machine is inseparable from professional programming support. G code, as the basic language of CNC programming, consists of a series of alphanumeric instructions to control every action of the machine tool. Although modern CAM software has greatly simplified the programming process, understanding the basic principles of G code is still an essential skill for CNC operators. Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software has become a key bridge between CAD design and CNC machining, automatically converting 3D models into tool paths and optimizing machining strategies.
The industrial value of CNC Machine is first reflected in its unparalleled machining accuracy and repeatability. Micron-level tolerances, which are difficult to achieve with traditional manual operations, have become standard on CNC machine tools. This precision machining capability directly determines the performance and reliability of the final product, especially in high-end manufacturing fields such as aerospace and precision instruments. At the same time, CNC technology has significantly improved manufacturing efficiency, reduced manual intervention through automated processing, achieved 24-hour continuous production, and significantly shortened product delivery cycles.

 English
English русский
русский